Swasthya Sankalp
A Holistic Approach to Hypertension and Diabetes Management
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as hypertension and diabetes are emerging as silent epidemics in India, with approximately 1 in 4 individuals experiencing elevated blood pressure and 1 in 7 facing high blood glucose levels. Recognizing the urgency of addressing this growing public health challenge, Project Swasthya Sankalp was as a collaborative initiative supported by Resolve to Save Lives (RTSL). The project aims to strengthen Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC) to prevent, detect early, and effectively manage these conditions at the grassroots level.
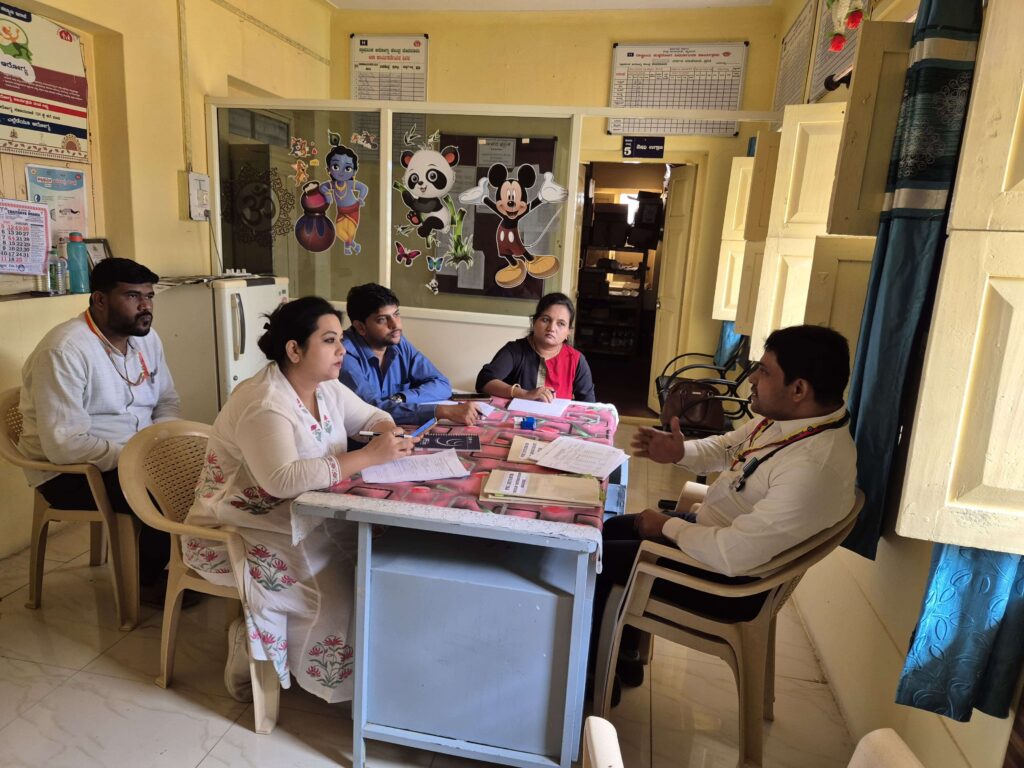

Spanning 27 districts across Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Karnataka, Swasthya Sankalp employs innovative strategies and community-centered solutions to tackle NCDs. Central to its approach is capacity building, which includes training medical officers, nurses, and Community Health Officers (CHOs) in updated clinical protocols and improving digital tools, such as the NCD portal, for efficient patient tracking. The project also emphasizes community engagement by screening at-risk individuals and promoting awareness of healthy lifestyle practices.
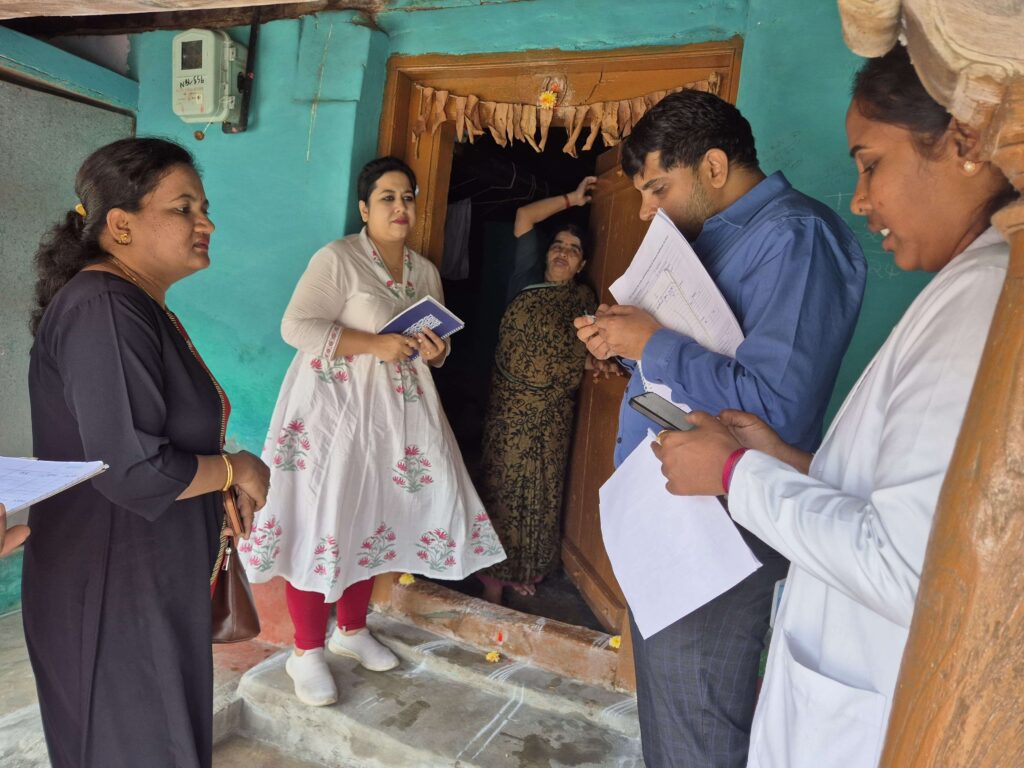

Additionally, Swasthya Sankalp strengthens systems by ensuring the availability of essential drugs and diagnostic tools, while closely collaborating with state governments to integrate sustainable practices into existing health programs. These efforts aim to create a scalable model for managing NCDs that can be replicated across other states and regions.
Through its collaborative approach with state governments, healthcare providers, and communities, Project Swasthya Sankalp seeks to reduce the burden of hypertension and diabetes. By doing so, it contributes significantly to India’s public health goals and aligns with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
